In today’s ever-changing economy, there are various sources of income that individuals can generate. One such source is unearned income. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of unearned income, exploring its definition, the different types it encompasses, as well as its benefits and drawbacks. Additionally, we will discuss how to calculate unearned income and provide strategies to maximize this form of income.
Unearned income, also known as passive income, is money obtained from sources other than employment, such as investments, rental properties, royalties, and dividends. It can be an attractive option for individuals looking to diversify their income streams, however, it also comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. By understanding the various types of unearned income and learning how to calculate and maximize this form of income, individuals can take strategic steps towards achieving financial stability and success. Join us as we explore the ins and outs of unearned income and its potential impact on your financial well-being.
Definition of unearned income
Unearned income refers to income that is not earned through work or employment. This type of income is typically generated from investments, rental property, royalties, and passive business activities. In other words, it is the income that is not directly tied to an individual’s effort or labor.
Examples of unearned income include interest from savings accounts, dividends from stocks, capital gains from the sale of assets, rental income from properties, and royalties from intellectual property.
It is important to distinguish unearned income from earned income, which is the income derived from wages, salary, and self-employment. Unearned income is often subject to different tax treatment than earned income, and it can play a significant role in a person’s overall financial situation.
Understanding the nature and sources of unearned income is crucial for financial planning and tax management, as it can impact an individual’s eligibility for certain government benefits and tax credits. Therefore, individuals should be aware of the various forms of unearned income and how they are treated under the tax laws.
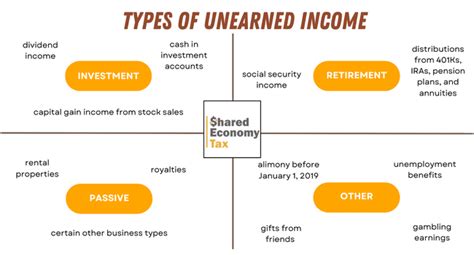
Types of unearned income
Unearned income comes in many forms and can be classified into several categories. One of the most common types of unearned income is interest income, which is earned from investments in savings accounts, certificates of deposit, or bonds. Another type is dividend income, which is generated from owning stocks in companies that pay out a portion of their profits to shareholders. Rental income is also considered unearned, as it is earned from owning property and leasing it to tenants. Finally, there is royalty income, which is obtained from owning the rights to patents, trademarks, or creative works and receiving payments for their use.
Each type of unearned income has its own unique characteristics and tax implications. Interest income is generally taxed at the individual’s ordinary income tax rate, while dividend income may receive preferential tax treatment. Rental income is subject to deductions for expenses related to the property, and royalty income is often taxed at a flat rate. Understanding the different types of unearned income is crucial for effective financial planning and tax management.
When it comes to managing unearned income, individuals may benefit from diversifying their investments to generate various types of unearned income. For example, someone with a large portion of their portfolio in stocks may also consider investing in bonds to generate interest income. Additionally, owning rental property can provide a steady stream of income separate from investment earnings. By diversifying the sources of unearned income, individuals can create a more stable and reliable financial foundation.
Overall, being aware of the different types of unearned income can help individuals make informed decisions about their investments and financial strategies. From interest and dividend income to rental and royalty income, each type offers unique benefits and considerations. By understanding these distinctions, individuals can make more informed choices about how to manage and maximize their unearned income.
Benefits and drawbacks of unearned income
Unearned income can provide individuals with financial stability and a source of passive income. This type of income includes interest, dividends, capital gains, and rental income, which can be beneficial for those looking to diversify their sources of revenue and build wealth over time.
On the other hand, unearned income can also have drawbacks, such as potential tax implications and fluctuations in investment returns. Individuals with unearned income may face higher tax rates on certain types of investment income, which can impact their overall financial picture. Additionally, unearned income is often dependent on market performance, which can be unpredictable and lead to variability in earnings.
Overall, unearned income offers the opportunity for financial growth and passive income generation, but it also comes with its own set of challenges and risks that individuals should consider when incorporating it into their financial strategy.
As such, it is important for individuals to carefully evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of unearned income and consider how it fits into their overall financial plan in order to make informed decisions about their investment and income strategies.
How to calculate unearned income
Unearned income is a term used to describe money that is received from sources other than employment. This type of income includes things like interest, dividends, and capital gains. To calculate unearned income, you will need to gather all of your investment and asset statements, including bank statements, brokerage statements, and any other documents that show income generated from investments.
Once you have gathered all of the necessary information, you can begin adding up the total amount of unearned income. This can include any interest or dividends that have been paid out to you, as well as any capital gains from the sale of assets. It’s important to make sure that you are including all sources of unearned income in your calculations, as leaving any out could result in an inaccurate total.
After adding up all of your unearned income sources, you will have the total amount of unearned income for the period in question. This can be used for budgeting purposes, tax calculations, or simply for tracking your overall financial situation. Keep in mind that unearned income is subject to different tax rules than earned income, so it’s important to understand how it will impact your overall financial picture.
Calculating unearned income can be a straightforward process if you have all of the necessary information at your disposal. By taking the time to gather your investment and asset statements, add up your sources of unearned income, and understand the implications of this type of income, you can ensure that you have a clear picture of your overall financial situation.
Strategies to maximize unearned income
Maximizing unearned income can be a key financial strategy for individuals looking to increase their overall income and achieve long-term financial stability. By taking advantage of various income-generating opportunities, individuals can build a diverse and resilient financial portfolio. One strategy to maximize unearned income is to invest in dividend-paying stocks and bonds. These investments can provide a steady stream of passive income, allowing individuals to grow their wealth without having to actively work for it.
Another effective strategy is to utilize real estate investments, such as rental properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs). By generating rental income or investing in income-producing properties, individuals can create a reliable source of unearned income. Additionally, individuals can explore the potential of peer-to-peer lending platforms, which offer opportunities to earn interest on loans to other individuals or small businesses.
Diversifying investments across various asset classes and industries can also help maximize unearned income. By spreading investments across different sectors, individuals can minimize risk and maximize potential returns. This approach can include investing in stocks, bonds, commodities, and alternative assets, ensuring a balanced and resilient investment portfolio.
Lastly, individuals can consider utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), to maximize unearned income. By taking advantage of tax-deferred or tax-free growth opportunities, individuals can increase their unearned income while minimizing their tax liabilities. This can be a powerful strategy for long-term financial growth and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is unearned income?
Unearned income refers to income that is not earned through employment or active participation in a business. It includes sources such as interest, dividends, rental income, and royalties.
What are the types of unearned income?
Types of unearned income include interest income, dividend income, rental income, capital gains, and royalties.
What are the benefits of unearned income?
Benefits of unearned income may include the potential for passive income, diversification of income sources, and the ability to build wealth without active work.
What are the drawbacks of unearned income?
Drawbacks of unearned income may include the fluctuation of investment returns, tax implications, and the potential for financial dependency on external sources of income.
How to calculate unearned income?
Unearned income can be calculated by adding up the income from interest, dividends, rental properties, capital gains, and any other sources of income that are not earned through active work or business operations.
What are some strategies to maximize unearned income?
Strategies to maximize unearned income may include diversifying investment portfolios, reinvesting dividends, leveraging tax-advantaged accounts, and engaging in passive income opportunities such as real estate investments.
Why is unearned income important for financial planning?
Unearned income is important for financial planning as it provides a means to supplement earned income, build long-term wealth, and achieve financial independence. It can also serve as a hedge against economic downturns and market volatility.